27-09-2024
Menopause can bring symptoms like hot flushes, difficulty sleeping, and mood problems - while it’s a totally natural change that usually begins to happen between 45 and 55, it’s a challenging time, affecting both physical and mental health. Menopause can also be brought on early by treatment for some medical conditions.
HRT, or hormone replacement therapy, is designed to treat these symptoms, which are caused by falling levels of the main female sex hormones, oestrogen and progesterone. Did you know falling levels of testosterone are also part of the menopause, contributing to a range of symptoms?
Here at Click Pharmacy we’ve broken down how different versions of HRT work, and have also used official statistics to see which NHS Trusts in England prescribe the most of these treatments.
How HRT works
The most frequently prescribed version of HRT is called continuous combined HRT. It contains both a synthetic oestrogen called estradiol, and a progestogen (a synthetic version of progesterone).
There are also tablets and patches that only use estradiol, but these are only suitable for women who have had a hysterectomy, as without a progestogen as well, the drug can increase the risk of endometrial cancer.
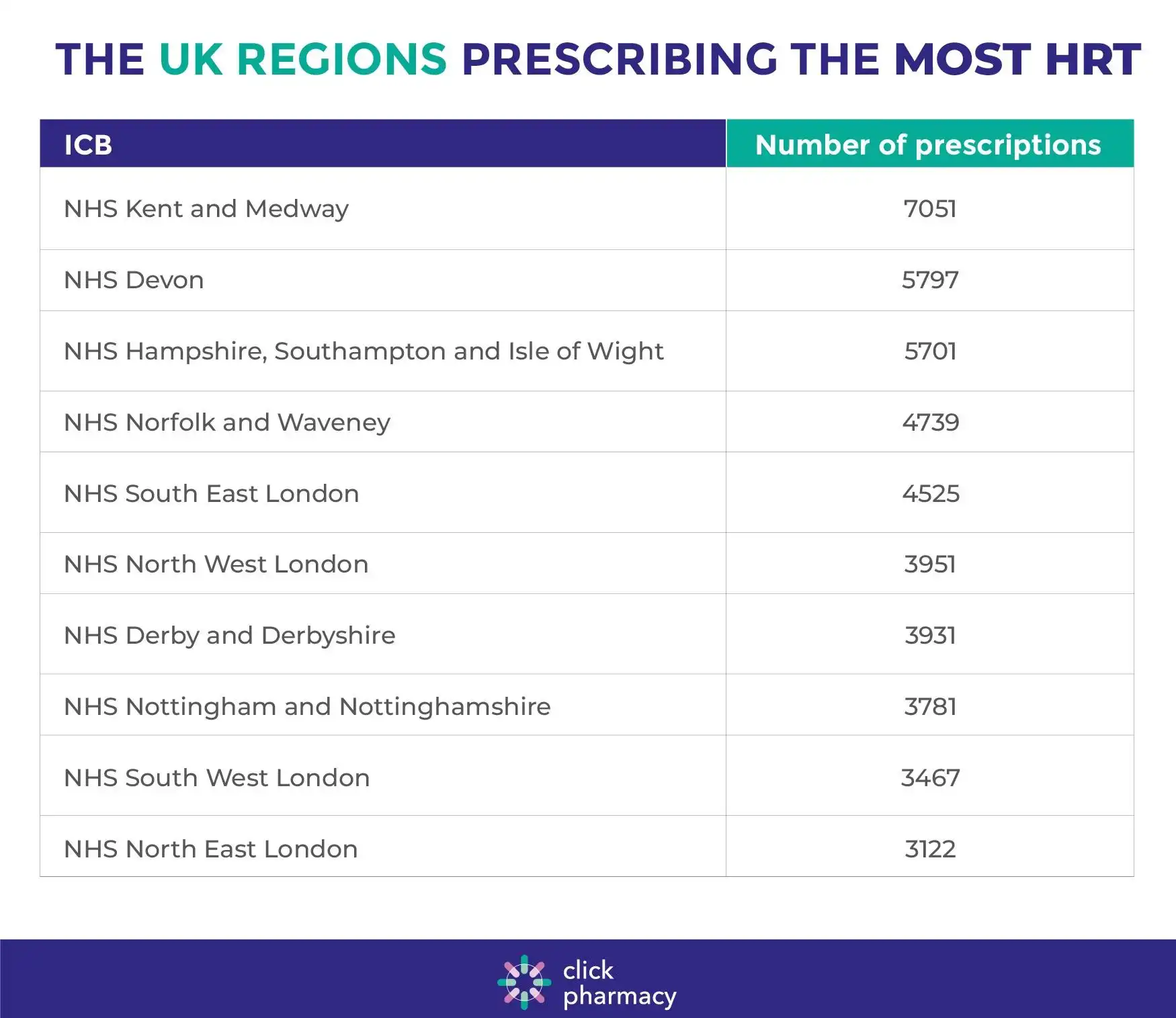
Overall, the NHS ICB that prescribed the most of all of the HRT treatments in our research was NHS Kent and Medway, where doctors made out 7051 prescriptions in June 2024. It was followed by NHS Devon with 5797 prescriptions. In third place with the next highest number of prescriptions was NHS Hampshire, Southampton and Isle of Wight, at 5701.
Combined continuous HRT
The combined continuous HRT methods in our research were Elleste Duet, Evorel Conti, Evorel Sequi, Femoston, Premique and Kliovance. Elleste Duet, Femoston, Premique and Kliovance are all tablets which are taken daily. Evorel Conti and Evorel Sequi are patches that you apply to your skin, and which slowly release a fixed dosage of hormones throughout the day.
Some people prefer patches to tablets because of the convenience, but others find that tablets are easier. Tablets are also the most common way to access HRT treatment.
Patches are prescribed to people who are at a higher risk of higher risk of blood clots or strokes. While oestrogen and synthetic versions of the hormone can slightly increase the risk of blood clots and strokes for some people, these medicines are safer when absorbed through the skin.
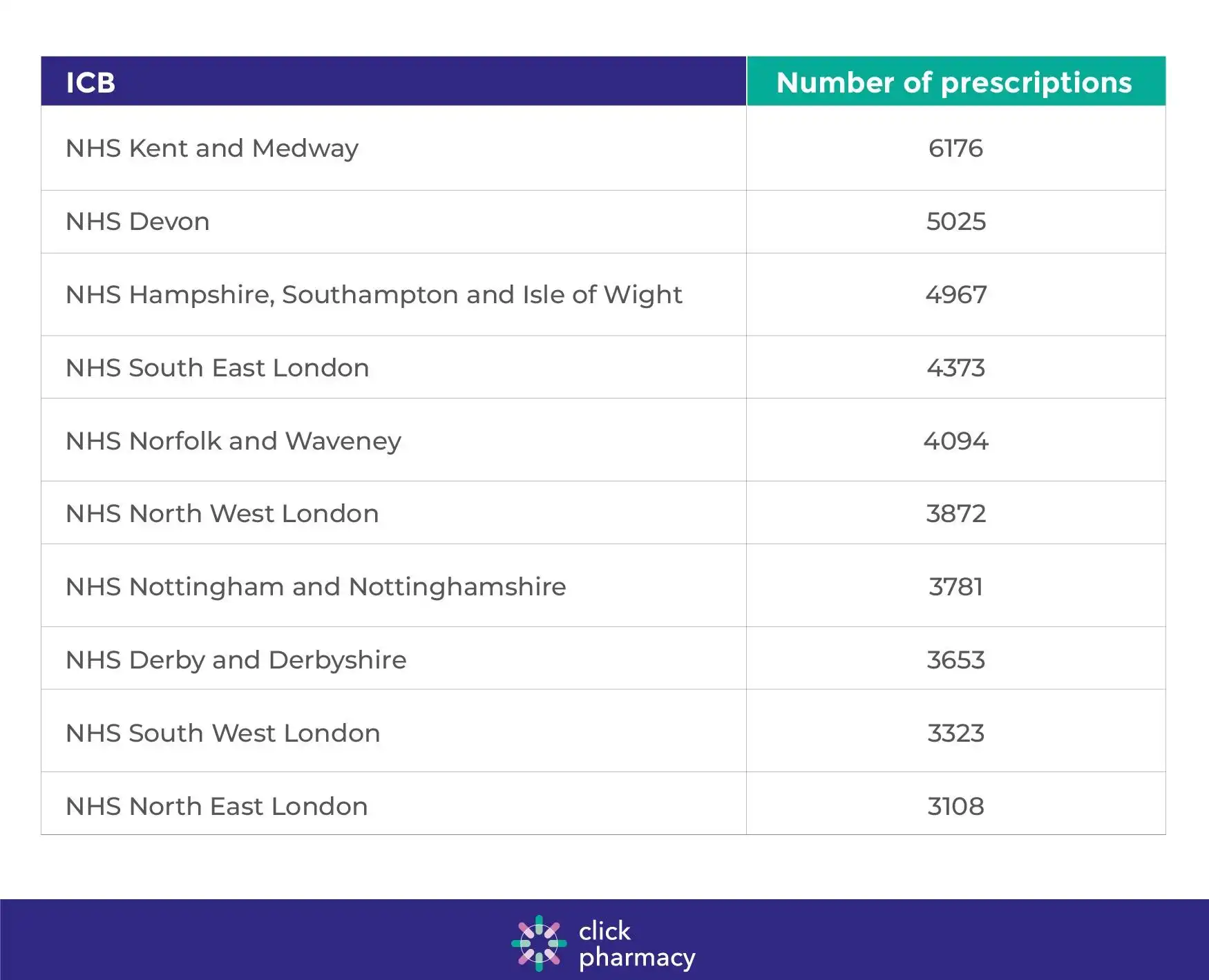
These were the top ten ICBs that prescribe the most continuous combined HRT treatments. As with the total figure of all HRT prescriptions, NHS Kent and Medway was at the top, with 6176 prescriptions made in the month of June 2024. NHS Devon was next with 5025 prescriptions, followed by NHS Hampshire, Southampton and Isle of Wight with 4967 prescriptions.
Oestrogen-only HRT
Oestrogen-only medications included in our research were Elleste Solo, Premarin and Zumenon, all of which are tablets that should be taken daily.
You can see that these medications are much less frequently prescribed compared to combined continuous HRT. This might be largely because only women who have had a hysterectomy can take these drugs without supplementing with progestogen treatments, making the number of people who are suitable patients for this treatment smaller. Women who have not had a hysterectomy can take these treatments as long as they take progestogen too, but it’s usually more convenient to take combined continuous HRT instead.
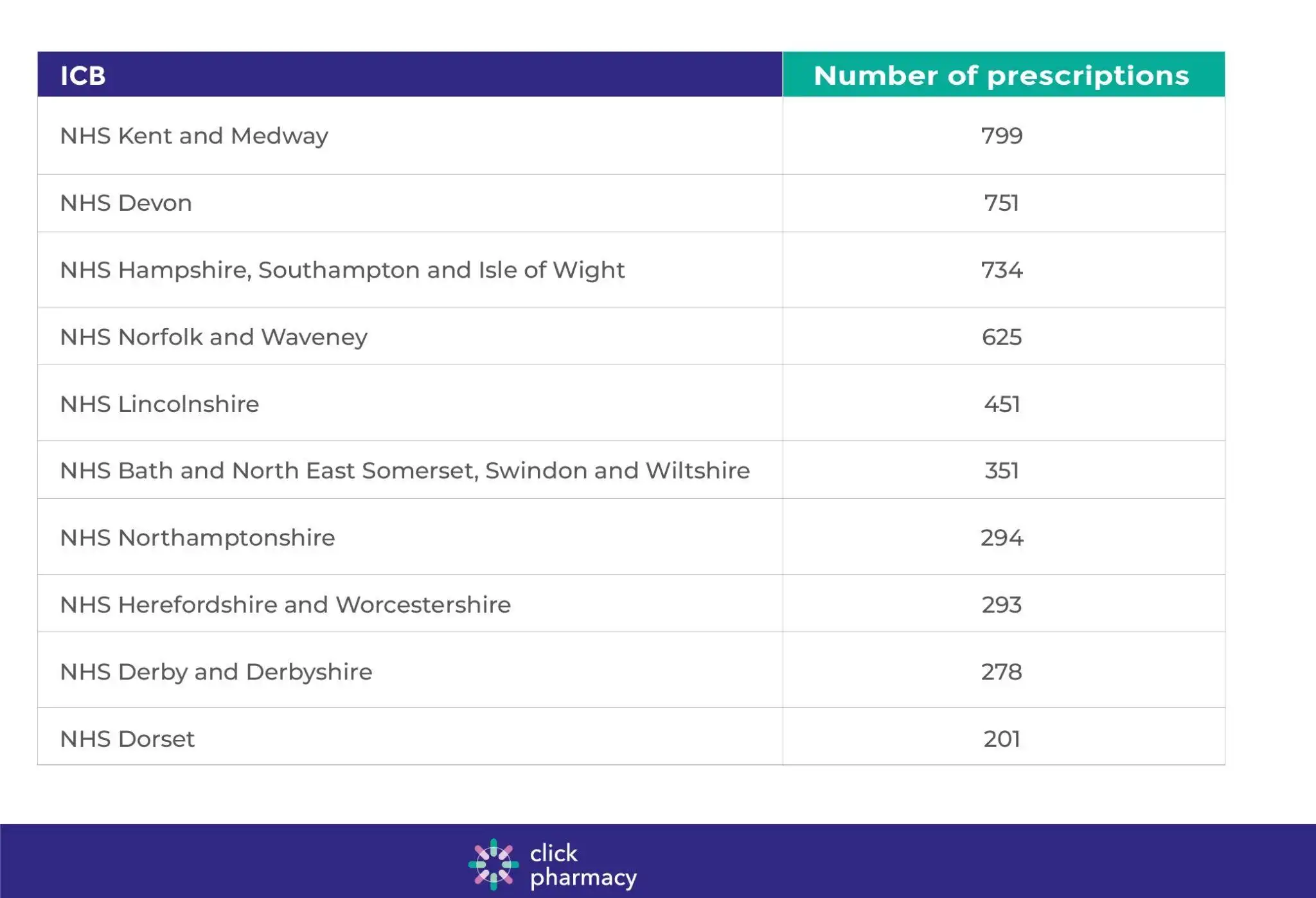
The number one prescriber of oestrogen-only HRT for menopausal women was NHS Kent and Medway, where 799 prescriptions were made out. The ICB where the second highest number of prescriptions was made out was NHS Devon, at 751. NHS Hampshire, Southampton and Isle of Wight was next, where doctors made out 734 prescriptions this June.
Livial
Livial, one of the drugs we looked at in our research, is different to some of the other HRT medications in this list. The key ingredient, tibolone, is a synthetic steroid that the body breaks down into compounds that mimic the effects of oestrogen, progesterone, and testosterone. Unlike other HRT drugs, its testosterone-like effects might have extra benefits for menopausal women who are experiencing symptoms associated with lowered testosterone, as well as limiting some of the side effects that other HRT methods can cause.
In the UK, testosterone can also be prescribed to women who are taking oestrogen-only or combined continuous HRT, as an additional treatment, usually if they describe symptoms like tiredness, low sex drive or difficulty concentrating. Lower levels of testosterone have been linked to all these symptoms. However, testosterone treatments like gel or cream will be prescribed ‘off-label’ under the supervision of your doctor, as they are not yet licensed to be used as treatment for menopause.
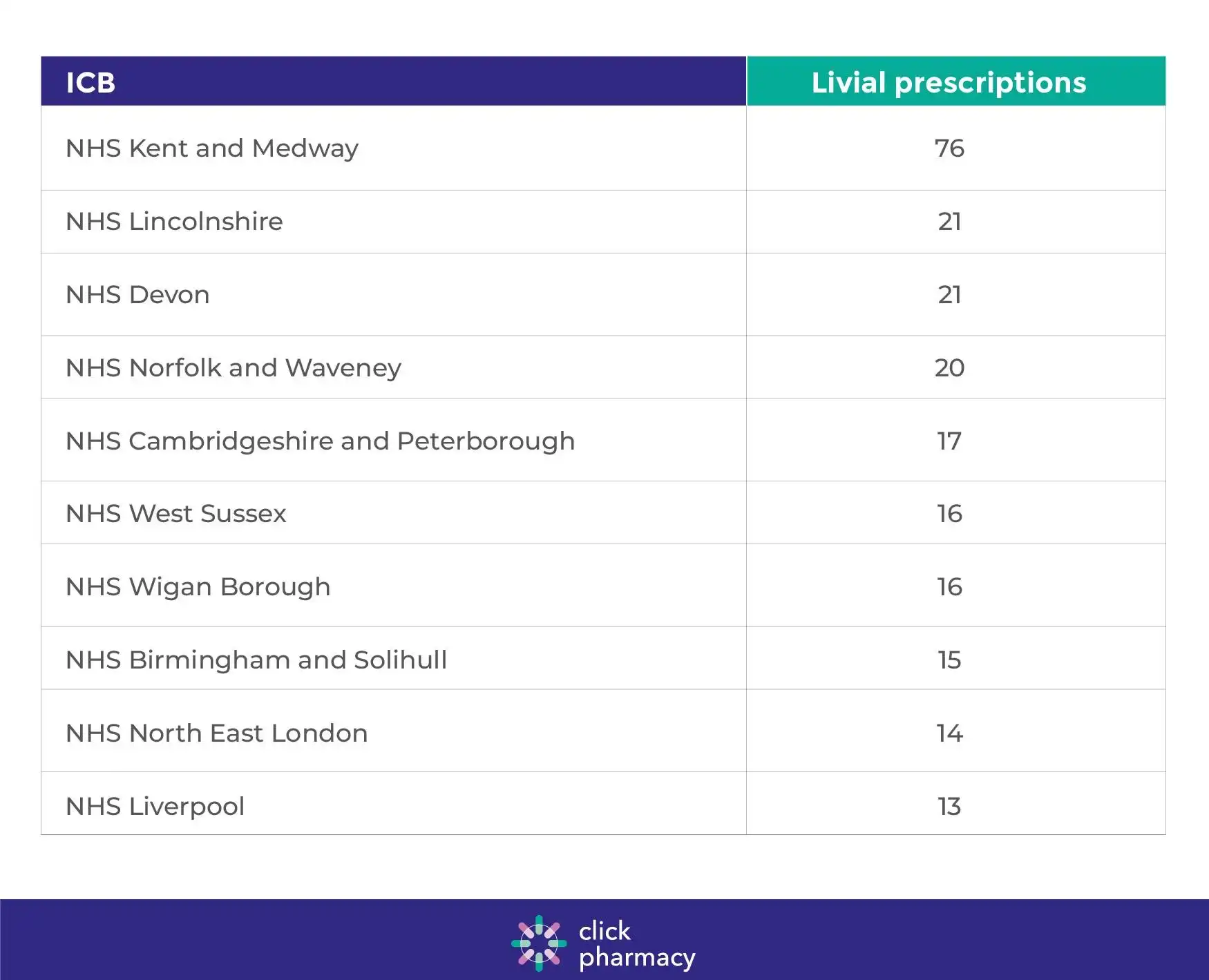
We looked into which NHS ICBs in England prescribed the most Livial in the month of June 2024, and saw that NHS Kent and Medway prescribed the highest number of prescriptions, at 76. This ICB was followed by NHS Lincolnshire and NHS Devon, where doctors made 21 prescriptions for Livial in each case.
Other HRT treatments
There are some treatments designed for the vagina, including creams and tablets that women can use to reduce dryness, lowering the risk of vaginal and urinary tract infections, as well as making sex more comfortable. These treatments include Estriol cream and Vagifem tablets. While these only include estriol or estradiol, they are safe to use without adding a progesteron because of the small amount of the hormone they include.
If you are experiencing menopause symptoms and you are considering hormone replacement therapy, we have a range of treatments available. Just fill in the medical assessment and we will check which medicine might be the best option for you.